Limites d’Azure Automation
- Timeout au bout de 3h, recommandation runner hybrid
- Impossible d’envoyer un msg Teams dans un canal depuis un Automation – fonctionne qu’en droit délégué, pas application
Installation module
Runtime Environment par défaut (Runtime 5.1)
Se rendre sur l’URL PowerShellGallery dédiée au module que l’on souhaite installer (avec la version spécifique).
Exemple : https://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/Microsoft.Graph.Beta.Identity.DirectoryManagement/2.28.0
Puis cliquer sur Deploy To azure Automation
Il est également possible de le faire en PowerShell :
Connect-AzAccount -SubscriptionId $subscriptionID -Tenant $tenantID
New-AzAutomationModule -AutomationAccountName $automationAccount -ResourceGroupName $RG -Name "Microsoft.Graph.Authentication" -ContentLinkUri "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/package/Microsoft.Graph.Authentication/2.29.1" -Verbose -RuntimeVersion "5.1"Runtime Environment dédié
Etape 1 : Créer un Runtime Environment dédié (ex : ‘PowerShell-5_1-DSCv2’)
Etape 2 : Importer un module à l’intérieur via PowerShell
Pour se faire, installer le module le permettant : Install-Module AzureResourceStuff
Puis exécuter la commande suivante :
Connect-AzAccount -SubscriptionId $subscriptionID -Tenant $tenantID
New-AzureAutomationRuntimeModule -moduleName $ModuleName -moduleVersion $ModuleVersion -runtimeName 'PowerShell-5_1-DSCv2' -resourceGroupName $RG -automationAccountName $automationAccount}Lien aide : https://doitpshway.com/managing-azure-automation-runtime-environments-via-powershell
Hybrid Runbook worker
Principe
In the current implementation of Private Link, Automation account cloud jobs cannot access Azure resources that are secured using private endpoint. For example, Azure Key Vault, Azure SQL, Azure Storage account, etc. To workaround this, use a Hybrid Runbook Worker instead. Hence, on-premises VMs are supported to run Hybrid Runbook Workers against an Automation Account with Private Link enabled.
Un Azure Automation ne peut pas taper sur une ressource interne via un Private Link
-> Use hybrid worker (VM) and set ut a Azure NAT GW with static public IP.
Then set all internet traffic from the VM/vNet to go through the GW to tag all outbound traffic with the GW IP
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/automation/how-to/private-link-security
Démo – Sortir par une IP fixe
Par défaut, il n’est pas possible de sortir par une IP fixe de son Automation.
De même, un Automation ne peut pas taper une ressource interne via un Private Link.
Cependant, en créant un Hybrid Runbook Worker, ces 2 actions sont possibles
Pour sortir du Automation depuis une IP fixe, les étapes sont les suivantes :
- Créer une VM dans Azure avec une IP publique rattachée à la carte réseau
- Créer un Azure Automation
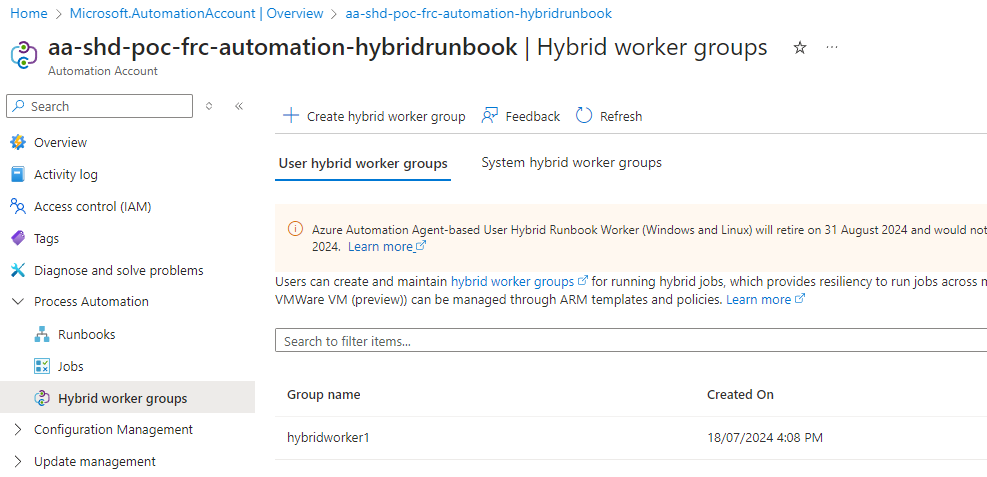
- Sur la Automation, dans Hybrid worker groups, faire une création en ajoutant la VM
- Le déploiement se fera automatiquement du runner sur la VM
- Pour tester, sur mon runbook, mettre le code suivant « (Invoke-WebRequest -uri « http://ifconfig.me/ip » -UseBasicParsing).Content «
- Lors du « Start », selectionner « Hybrid worker »
Exemple :
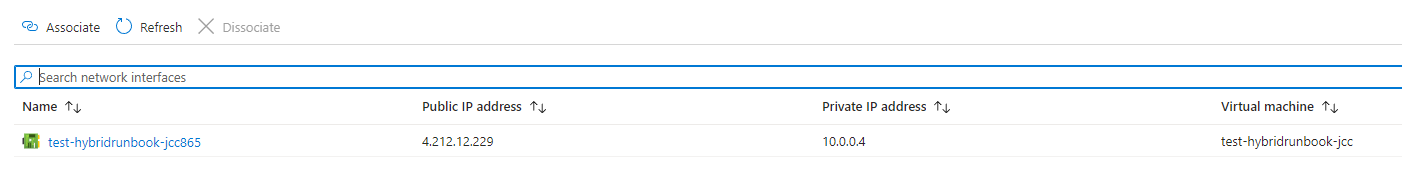
IP machine virtuelle :
Configuration du Runbook worker :
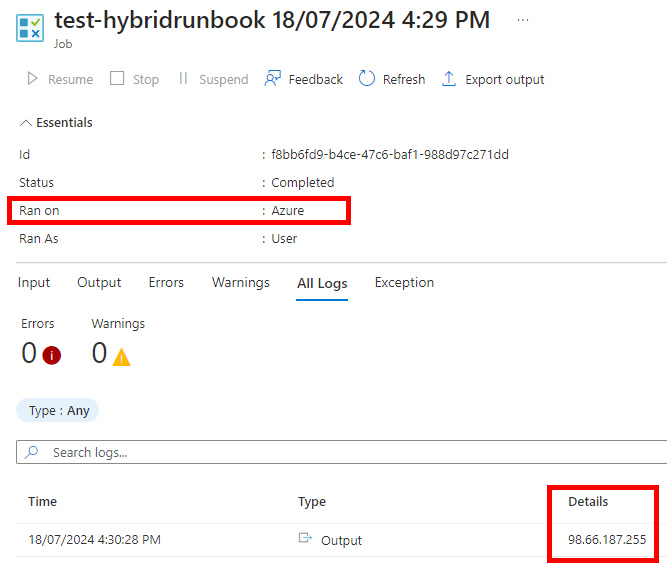
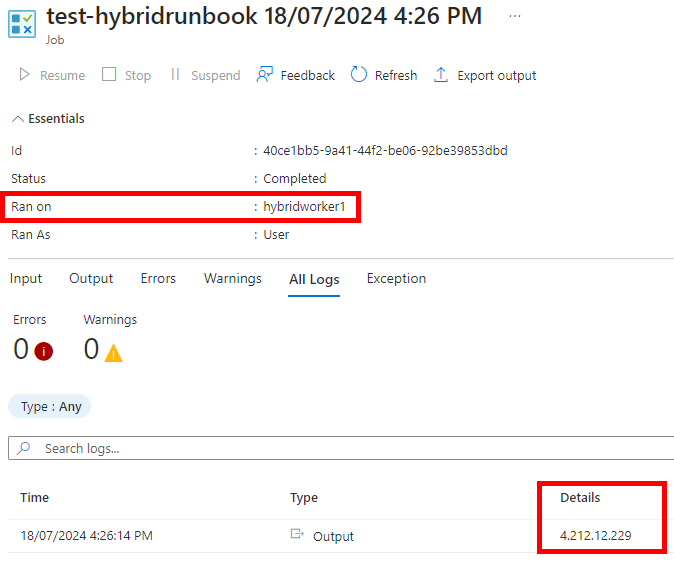
Lors de l’exec depuis le runner, on a bien l’IP de la VM :
Lors de l’exec depuis le Automation, on a une IP random :